C#.NET使用客户端缓存提高API性能
当前位置:点晴教程→知识管理交流
→『 技术文档交流 』
摘要在现代应用程序中,性能始终是一个关键的考虑因素。无论是提高响应速度,降低延迟,还是减轻服务器负载,开发者都在寻找各种方法来优化他们的API。在Web开发中,利用客户端缓存是一种有效的方法,可以显著提高API的性能。本文将结合Replicant和Delta,深入探讨如何在.NET中使用客户端缓存,巧妙地提升API的响应速度。 问题概述尽管数据库已经过优化,但在实际应用中,我们仍然会遇到一些性能瓶颈。例如,当数据库中有数百万条记录时,即使添加了索引,某些查询(如对用户名的部分匹配搜索)仍可能导致响应延迟。在API集成中,每次请求都需要花费较长的时间,这不仅影响用户体验,还会增加服务器的负载。 解决方案概述为了应对这些性能挑战,我们可以采用以下策略:
接下来,我们将详细探讨如何在.NET中实现上述策略,并提供具体的代码示例。 客户端缓存概述什么是HTTP缓存头?HTTP提供了一系列头信息,用于管理缓存行为。这些头信息包括:
通过合理地设置这些头信息,客户端和服务器可以协同工作,实现高效的缓存机制。 浏览器中的缓存机制当浏览器发送请求时,如果服务器返回了 在HTTP客户端中实现缓存在非浏览器环境(如使用 使用Delta优化服务器端缓存什么是Delta?Delta是一个开源的.NET库,通过在数据库中添加一个版本列(如 如何使用Delta?
Delta的工作原理
使用Delta的优势
使用Replicant实现HTTP客户端缓存什么是Replicant?Replicant是由Simon Cropp开发的一个开源.NET库,用于实现HTTP客户端的缓存机制。它利用了与浏览器相同的HTTP缓存头(如 使用Replicant的步骤
Replicant的工作原理
综合示例:提升API集成请求性能下面,我们将结合Replicant和Delta,提供一个完整的示例,展示如何利用客户端和服务器端缓存,提高API的性能。 后端代码示例以下是使用Delta库的后端代码示例。该示例中,我们构建了一个简单的博客应用,包含了博客(Blog)和帖子(Post)两个实体。 1. 配置 |
| using Delta; | |
| using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; | |
| using System.Text.Json; | |
| using System.Text.Json.Serialization; | |
| using TutorialClientCache.Components; | |
| var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); | |
| builder.AddNpgsqlDbContext<BloggingContext>("mydb"); | |
| // 添加服务到容器 | |
| builder.Services.AddRazorComponents() | |
| .AddInteractiveWebAssemblyComponents(); | |
| builder.Services.AddBootstrapBlazor(); | |
| var app = builder.Build(); | |
| // 使用Delta中间件 | |
| app.UseDelta<BloggingContext>(); | |
| // 定义API端点 | |
| app.MapGet("/posts", async (string? title, BloggingContext db) => | |
| { | |
| var query = db.Posts | |
| .Where(p => title == null || p.Title.Contains(title)) | |
| .OrderByDescending(p => p.Title) | |
| .ThenBy(p => p.Content) | |
| .Take(10); | |
| return await query.ToListAsync(); | |
| }); | |
| // 配置HTTP请求管道 | |
| if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment()) | |
| { | |
| app.UseWebAssemblyDebugging(); | |
| } | |
| else | |
| { | |
| app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error", createScopeForErrors: true); | |
| } | |
| app.UseAntiforgery(); | |
| app.MapStaticAssets(); | |
| app.MapRazorComponents<App>() | |
| .AddInteractiveWebAssemblyRenderMode() | |
| .AddAdditionalAssemblies(typeof(TutorialClientCache.Client._Imports).Assembly); | |
| app.Run(); |
数据上下文 BloggingContext
public class BloggingContext : DbContext
{
public BloggingContext(DbContextOptions<BloggingContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
}
实体类 Blog 和 Post
public class Blog
{
public int BlogId { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
public List<Post> Posts { get; } = new List<Post>();
}
public class Post
{
public int PostId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public int BlogId { get; set; }
public Blog Blog { get; set; }
}
由于浏览器HttpClient已经内置客户端缓存逻辑,这里提供一个可以在其他Runtime环境内使用缓存的例子:
// See https://aka.ms/new-console-template for more information
using Replicant;
using System.Diagnostics;
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!");
string url = "http://localhost:5225/posts?title=CSS";
//warm up
await MeasureHttpClientPerformance(url);
await MeasureHttpCachePerformance(url);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
var httpClientTime = await MeasureHttpClientPerformance(url);
Console.WriteLine($"HttpClient Time: {httpClientTime} ms");
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
var httpCacheTime = await MeasureHttpCachePerformance(url);
Console.WriteLine($"HttpCache Time: {httpCacheTime} ms");
}
static async Task<long> MeasureHttpClientPerformance(string url)
{
using var httpClient = new HttpClient();
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var response = await httpClient.GetAsync(url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
stopwatch.Stop();
return stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
static async Task<long> MeasureHttpCachePerformance(string url)
{
HttpCache cachedClient = HttpCache.Default;
var stopwatch = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var response = await cachedClient.ResponseAsync(url);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
var content = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
stopwatch.Stop();
return stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
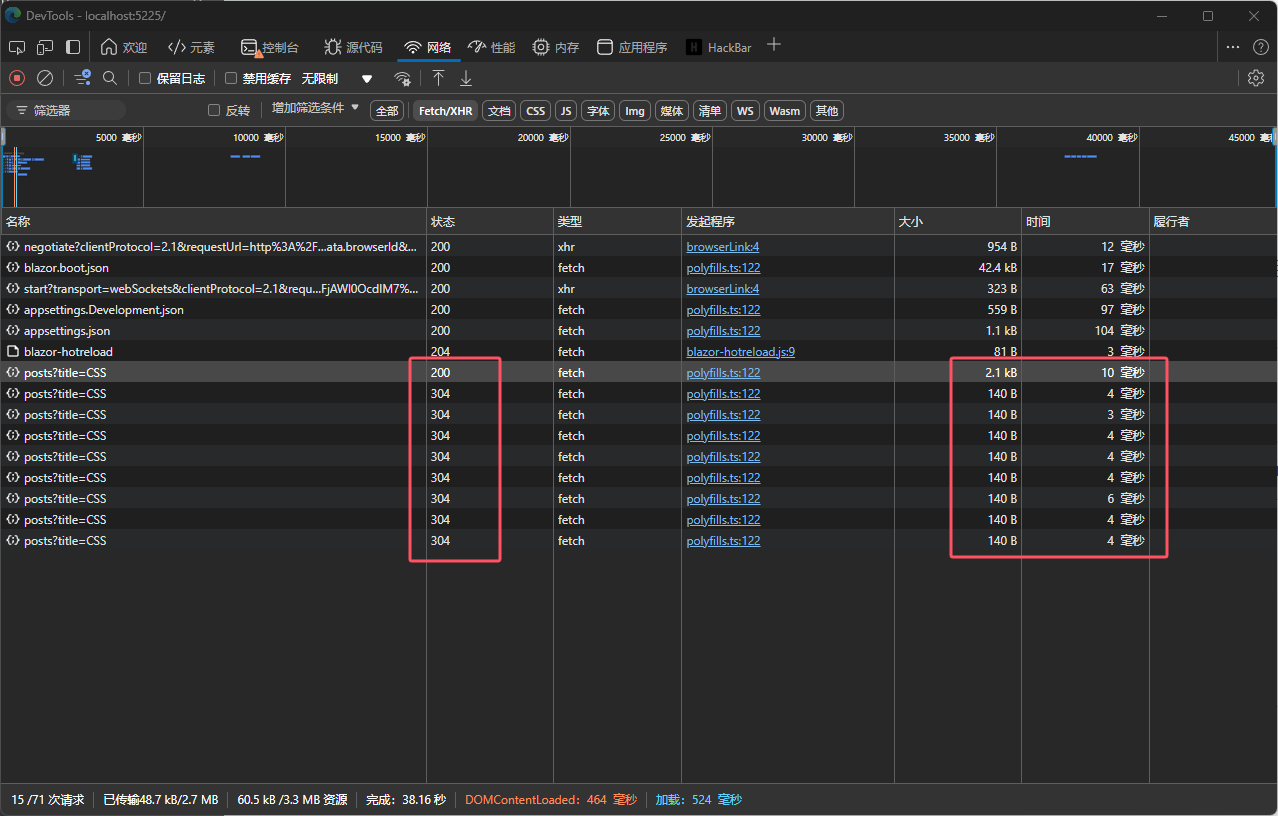
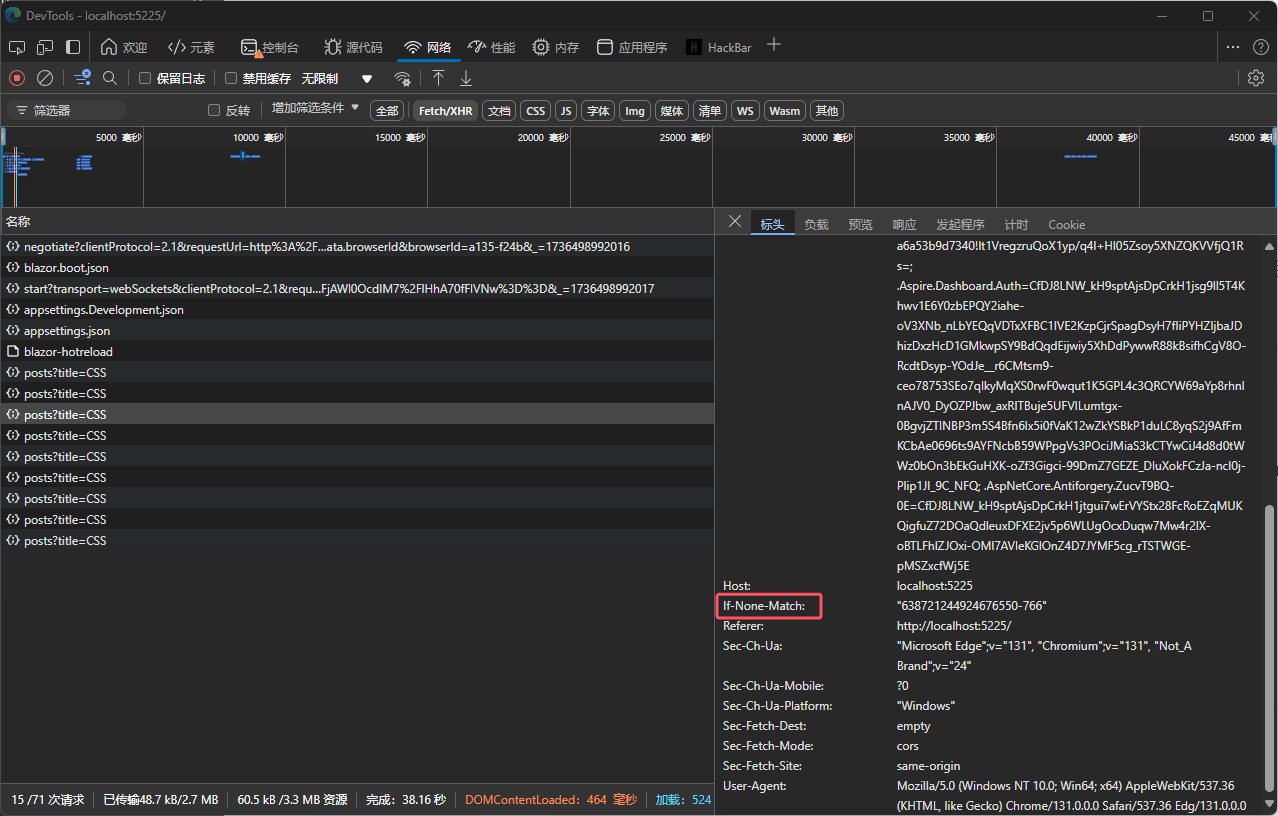
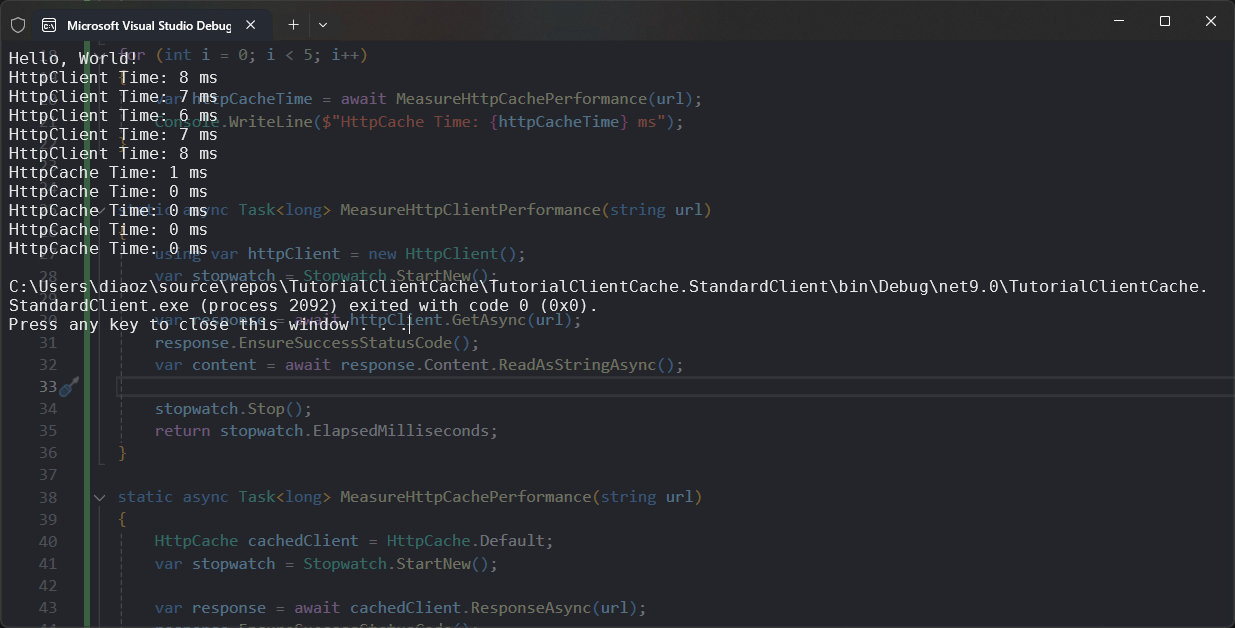
通过结合使用Delta和Replicant,我们可以在.NET应用程序中有效地利用客户端缓存机制,显著提升API的性能。利用ETag和304 Not Modified等HTTP特性,我们能够减少不必要的网络请求和数据传输,提高应用的响应速度和用户体验。
转自https://www.cnblogs.com/madtom/p/18664378